Punicalagin vs. Ellagic Acid: Key Differences in Pomegranate Peel Extract for Skincare Formulations
2025-10-21 09:51:14
If you're in the skincare game, whether whipping up formulations in a lab or sourcing raw materials for your next big product launch, you've probably heard the buzz around pomegranate peel extract. This powerhouse ingredient, derived from the often-overlooked outer layer of Punica granatum, is loaded with bioactive compounds that can elevate your serums, creams, and lotions to the next level.
But here's the thing—not all components in pomegranate peel extract are created equal. Punicalagin and ellagic acid stand out as the heavy hitters, yet they bring different strengths to the table when it comes to antioxidant protection, skin brightening, and overall efficacy in cosmetic recipes. How do we choose active ingredients in our cosmetics formulations?
As a leading producer of high-purity pomegranate peel extract powder, Xi An Chen Lang Bio Tech Co., Ltd., we've seen firsthand how choosing the right one—or blending them strategically—can make or break a product's performance. In this article, we'll break down differences between punicalagin and ellagic acid from pomegranate peel, from chemical makeup to ideal dosages, so you can make smarter decisions for your formulations. Stick around, and you'll see why our product standardized for optimal punicalagin content, is becoming a go-to for brands chasing clean, effective skincare solutions.
Chemical Structure and Composition
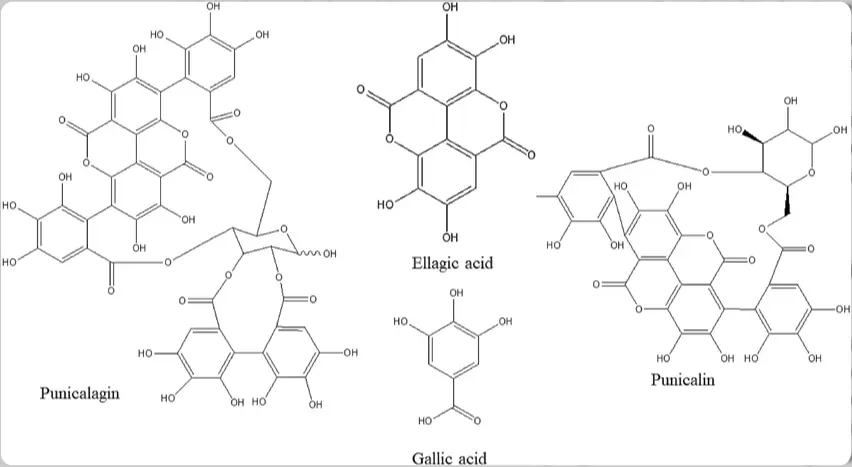
Let's start with the basics—what these compounds actually look like under the microscope. Punicalagin is a hefty ellagitannin, essentially a complex tannin with a molecular formula of C₄₈H₂₈O₃₀ and a weight around 1084 g/mol. It's made up of gallic acid units hooked onto a glucose core, giving it that bulky, polymeric vibe.
This structure makes it super water-soluble, which is a win for formulating aqueous-based products like gels or serums. On the flip side, ellagic acid is the sleeker cousin—a dilactone polyphenol with the formula C₁₄H₆O₈ and a lighter 302 g/mol. Think of it as two gallic acid molecules fused together, forming a more compact ring system. While both are hydrophilic, ellagic acid's simpler setup means it can sometimes crystallize out in high concentrations, potentially affecting texture in your end product.
Why does this matter for skincare formulations? Punicalagin's larger size acts like a slow-release reservoir—it hydrolyzes over time into ellagic acid and other goodies, providing sustained benefits. In pomegranate peel extract, punicalagin often dominates, making up the bulk of the polyphenolic punch. At Xi An Chen Lang Bio Tech Co., Ltd., our pomegranate peel extract is standardized to 40-60% punicalagin, ensuring you get that robust structure without the guesswork. Ellagic acid, meanwhile, shines in quicker-acting formulas but might need stabilizers to prevent precipitation. If you're crafting a brightening cream, punicalagin's complexity could mean longer-lasting antioxidant effects, while ellagic acid offers a more direct hit.
Sources and Occurrence in Pomegranate Peel
Both compounds are abundant in pomegranate peel, which is often discarded as waste but is actually the richest part of the fruit in polyphenols.
Punicalagin: Highly specific to pomegranates, where it's found predominantly in the peel as alpha- and beta-punicalagin. It's also present in lesser amounts in related plants like Terminalia species, but pomegranate peel is the main commercial source.
Ellagic Acid: More widely distributed across fruits (e.g., berries, nuts) and vegetables, but in pomegranates, it's primarily derived from the hydrolysis of ellagitannins like punicalagin. Free ellagic acid levels in the peel can vary, but it's often present alongside or as a metabolite of punicalagin.
In extraction processes, punicalagin dominates fresh pomegranate peel extracts, while ellagic acid may increase if the extract is hydrolyzed (e.g., via heat, enzymes, or gut bacteria).
Metabolism and Bioavailability: How They Work in the Skin
Here's where things get interesting for topical applications. Punicalagin boasts impressive bioavailability—up to 95% absorption—because it breaks down stepwise into ellagic acid and then urolithins via skin enzymes or microbiome. This cascade means deeper penetration and longer-lasting action, ideal for anti-aging serums that need to combat oxidative stress over hours. Ellagic acid, with its lower direct absorption (around 10% gets through unchanged), relies more on those metabolites for efficacy, but it can act faster on the surface layers.
In skincare formulations, this translates to punicalagin being a star for barrier-repair creams, where sustained release helps soothe inflammation from environmental aggressors. Studies show punicalagin reduces hydrogen peroxide levels in skin cells more effectively, slashing oxidative damage. Ellagic acid excels in spot treatments for hyperpigmentation, as it directly inhibits tyrosinase without the wait. Blending them in pomegranate peel extract maximizes both—quick wins from ellagic acid plus endurance from punicalagin.
Comparison Table
|
Aspect |
Punicalagin |
Ellagic Acid |
|
Molecular Formula |
C₄₈H₂₈O₃₀ |
C₁₄H₆O₈ |
|
Molar Mass |
1084.71 g/mol |
302.197 g/mol |
|
Type |
Ellagitannin (complex tannin) |
Polyphenol (dilactone) |
|
Relation |
Precursor; hydrolyzes to ellagic acid |
Breakdown product of ellagitannins |
|
Bioavailability |
High (up to 95% absorption) |
Low (90% unabsorbed) |
|
Antioxidant Strength |
Higher (superior in multiple assays) |
Lower in direct comparisons |
|
Key Sources |
Pomegranate peel (specific) |
Widespread in fruits/nuts |
|
Toxicity |
None observed in high doses |
Not specified; generally safe |
Antioxidant Activity and Biological Effects
Both offer antioxidant benefits, but punicalagin generally outperforms ellagic acid in potency and versatility:
Punicalagin: Exhibits superior antioxidant activity, as shown in studies comparing pomegranate extracts. It ranks high in assays like ORAC, TEAC, FRAP, and DPPH, scavenging free radicals more effectively. It also inhibits enzymes like carbonic anhydrase and has shown no toxicity in animal studies (e.g., 6% diet in rats for 37 days). Potential health benefits include cardiovascular support, glycemic control, oral health, and skin protection, with clinical evidence from standardized extracts.
Ellagic Acid: Provides antioxidant effects but at lower levels than punicalagin in pomegranate contexts. Its metabolites (urolithins) show estrogenic and antiestrogenic activities. While marketed for anti-cancer and heart health benefits, there's no robust scientific evidence, and the FDA has warned against false claims for it as a "fake cancer cure."
Research indicates punicalagin may be more effective at inducing apoptosis (cell death) in cancer cells and reducing inflammation compared to ellagic acid.
Skin-Specific Benefits: Brightening, Anti-Aging, and Beyond
Diving into efficacy for skincare, punicalagin and ellagic acid both tackle inflammaging—that sneaky combo of inflammation and aging—but in nuanced ways. Punicalagin calms redness and promotes collagen via fibroblast stimulation, making it a hero for anti-wrinkle lotions. Research on fibroblasts shows it boosts viability at low doses, enhancing firmness and elasticity. Ellagic acid focuses on whitening, inhibiting melanin production to fade dark spots, and offers UV repair, cutting erythema post-exposure.
In formulations, punicalagin suits multi-taskers like all-in-one serums for overall glow, while ellagic acid fits hyperpigmentation masks. Pomegranate peel extract combining both reduced forehead lines and improved skin radiance in studies. At Xi An Chen Lang Bio Tech Co., Ltd., our pomegranate peel extract delivers these benefits in a stable, natural form, helping brands create products that users rave about for visible results.
Formulation Differences: Compatibility and Stability Tips
When it comes to mixing into cosmetics, punicalagin's stability in water-based systems makes it versatile for gels and emulsions—pair it with humectants like glycerin for seamless integration. It's less prone to degradation, holding up in pH 4-7 ranges. Ellagic acid, being smaller, dissolves well but can oxidize faster, needing antioxidants like vitamin C to stay potent.
For pomegranate peel extract, start with punicalagin-dominant versions for oil-in-water lotions; ellagic acid-heavy for quick-absorb serums. Compatibility-wise, both play nice with niacinamide or hyaluronic acid, but test for interactions. Our team at Xi An Chen Lang Bio Tech Co., Ltd. offers custom blends, ensuring your formulas are stable and effective.
Recommended Dosages: Getting the Balance Right
Dosage is key to avoiding irritation while maximizing benefits. For punicalagin in pomegranate peel extract, aim for 0.1-7.5% in serums (standardized to 10-30% punicalagin), with studies showing efficacy at 10^-5 to 10^-8 M for cell vitality. Ellagic acid works at 0.5-1% topically, or 100mg/day orally for pigmentation perks. In extracts, ratios vary—our 40% punicalagin pomegranate peel extract allows flexible dosing for brightening without overload.
Always patch-test and comply with regs; higher punicalagin means fewer additives for clean formulas.
Conclusion: Why Pomegranate Peel Extract Is Your Next Must-Have
Wrapping it up, punicalagin edges out ellagic acid in potency and versatility for skincare formulations, but together in pomegranate peel extract, they create unbeatable synergy for brightening, protecting, and rejuvenating skin. As the clean beauty trend surges, sourcing high-quality extracts like ours at Xi An Chen Lang Bio Tech Co., Ltd. gives you an edge—our pomegranate peel extract comes in 40% and 60% punicalagin purities, with full certifications and bulk options for seamless scaling.
Ready to level up your products? Drop us a line at admin@chenlangbio.com for samples, quotes, or custom formulations. We're here to help you craft skincare that not only works but wows your customers.
References
1.Punica granatum L. (Pomegranate) Extracts and Their Effects on Healthy and Diseased Skin - PMC
2.Bioactive potential of punicalagin: A comprehensive review
3.Effect of Punicalagin and Ellagic Acid on Human Fibroblasts In Vitro
4.Efficacy and Safety of a Proprietary Punica Granatum Extract
5.Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) Extract Effects on Inflammaging
6.A punica granatum extract and its cosmetic uses - Patents
7.Biodegradation of Punicalagin into Ellagic Acid
8.Effects of Oral Administration of Ellagic Acid-Rich Pomegranate Extract
Send Inquiry
Related Industry Knowledge
- Punicalagin vs. Ellagic Acid: Key Differences in Pomegranate Peel Extract for Skincare Formulations
- How Does Liposomal Coenzyme Q10 Work?
- What Precautions Should be Taken When Handling D-Luciferin Potassium Salt?
- How Long Does Sildenafil Powder Last? Effects and Duration
- What is An Alternative to Monobenzone
- What is the Best Ergothioneine Supplement
- What Is Praziquantel Used for in Fish
- Unlocking the Benefits Understanding the Uses of TUDCA
- What is Green Tea Extract EGCG Powder Used For
- What is Cnidium Monnieri Fruit Extract Used for