What is the Chemical Structure and Formula of Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate?
2025-03-27 10:20:37
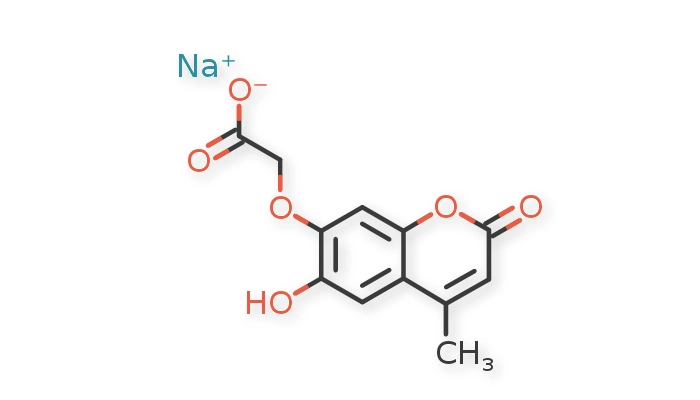
Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate (SMA) is a natural compound derived from the root of the Scoparia dulcis plant with significant pharmacological potential. This bioactive coumarin derivative has a distinctive chemical structure characterized by a benzopyran core with specific functional groups attached. The molecular formula of Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate is C₁₂H₉NaO₆ with a molecular weight of 272.19 g/mol. Its chemical name is sodium [(6-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran-7-yl)oxy]acetate, featuring a benzopyran ring system with hydroxyl, methyl, and sodium acetate functional groups strategically positioned to confer its unique biological properties.
The Molecular Composition and Properties of Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate
Chemical Structure Breakdown and Functional Groups
Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate possesses a complex molecular architecture centered around a coumarin scaffold. The core structure consists of a benzopyran system (2H-1-benzopyran) with a carbonyl group at position 2 (making it 2-oxo) and a methyl group at position 4. What distinguishes Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate from other coumarin derivatives is the presence of a hydroxyl group at position 6 and an oxyacetate sodium salt functionality at position 7. This unique arrangement of functional groups contributes to its impressive pharmacological profile. The sodium salt formation enhances water solubility compared to the free acid form, making it more bioavailable for various applications. The electron-rich nature of the aromatic ring, coupled with the strategic positioning of oxygen-containing functional groups, enables Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate to interact effectively with various biological targets, particularly enzymes involved in inflammatory and oxidative stress pathways. The methyl group at position 4 contributes to the compound's lipophilicity, influencing its ability to penetrate cellular membranes. Together, these structural features create a molecule with balanced hydrophilic and lipophilic properties, optimizing its therapeutic potential.
Physical and Chemical Characteristics
Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate appears as a light grey amorphous powder at room temperature, reflecting its molecular organization in the solid state. Its molecular weight of 272.19 g/mol places it in the range of moderate-sized bioactive compounds, facilitating cellular penetration while maintaining sufficient complexity for specific biological interactions. The compound exhibits excellent stability under normal storage conditions, maintaining its efficacy over extended periods when properly stored. Its solubility profile is particularly advantageous for pharmaceutical and cosmetic applications - the sodium salt form enhances water solubility while maintaining sufficient lipophilicity for effective absorption. The compound's melting point and thermal stability characteristics make it suitable for incorporation into various formulation types, from aqueous solutions to emulsions and solid dosage forms. Spectroscopic analysis reveals distinctive absorption patterns that can be used for identification and purity assessment, with characteristic peaks in UV-visible and infrared spectra corresponding to its coumarin core structure and functional group arrangement. The compound's chemical reactivity is primarily governed by the presence of phenolic hydroxyl groups, which can participate in hydrogen bonding and redox reactions, contributing to its antioxidant properties and biological activity profile.
Biosynthetic Origin and Natural Sources
Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate's journey begins in the biosynthetic pathways of the Scoparia dulcis plant, commonly known as sweet broom or scoparia weed. This medicinal plant has a long history of use in traditional medicine systems across tropical regions. The biosynthesis of Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate follows the general coumarin pathway, beginning with the shikimate pathway that produces phenylalanine. Through a series of enzymatic transformations involving hydroxylation, glycosylation, and specific methylation steps, the plant produces esculetin derivatives that are further modified to yield methylesculetin. The final acetylation and salt formation steps may occur during the extraction and purification process. The concentration of Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate varies across different parts of the Scoparia dulcis plant, with the roots typically containing the highest levels. Environmental factors significantly influence the production of this compound, with stress conditions often enhancing its biosynthesis as part of the plant's defense mechanism. At Chen Lang Bio, rigorous selection criteria ensure that only the highest quality plant materials are used for extraction, considering factors such as harvest time, growth environment, and absence of diseases or pests. This careful attention to raw material quality, combined with advanced extraction technologies including dynamic countercurrent extraction and column separation techniques, ensures a consistent and high-purity Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate product.
How does Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate function in oral care products?
Antimicrobial and Anti-inflammatory Mechanisms
Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate exhibits remarkable antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties that make it an invaluable ingredient in modern oral care formulations. The compound's antimicrobial action stems from its ability to disrupt bacterial cell membranes and interfere with essential metabolic processes in oral pathogens. Research has demonstrated its effectiveness against common oral bacteria associated with dental caries and periodontal disease, including Streptococcus mutans and Porphyromonas gingivalis. What makes Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate particularly valuable is its selective action, which targets harmful bacteria while preserving beneficial components of the oral microbiome. On the anti-inflammatory front, Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate works through multiple mechanisms, with one of the most significant being the inhibition of myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity. MPO is an enzyme released by activated neutrophils during inflammation and produces hypochlorous acid, which can damage surrounding tissues if overactive. By modulating MPO activity, Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate helps control excessive inflammatory responses in oral tissues. Additionally, the compound reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, particularly interleukin-6 (IL-6), which plays a central role in gingival inflammation. This multi-targeted approach to inflammation control makes Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate particularly effective for managing conditions like gingivitis and periodontitis, where chronic inflammation contributes to tissue destruction and disease progression.
Antioxidant Action and Tissue Protection
The oral cavity is constantly exposed to oxidative stressors from various sources, including diet, environmental factors, and the metabolic activities of oral microorganisms. Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate offers powerful antioxidant protection through several complementary mechanisms. Its chemical structure, particularly the phenolic hydroxyl groups, enables direct scavenging of reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as superoxide radicals, hydroxyl radicals, and hydrogen peroxide. This direct neutralization of free radicals prevents oxidative damage to oral tissues, including gingiva, periodontal ligaments, and tooth structures. Beyond direct scavenging, Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate enhances the body's endogenous antioxidant defenses by activating nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a master regulator of cellular antioxidant responses. This activation triggers the expression of cytoprotective enzymes like superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase, creating a comprehensive antioxidant shield. The compound's ability to chelate metal ions, particularly iron and copper, further contributes to its antioxidant profile by preventing these metals from catalyzing harmful oxidative reactions. This multi-dimensional antioxidant activity makes Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate particularly effective in preventing oxidative stress-related oral conditions, including periodontal disease progression and the development of potentially malignant disorders. Clinical studies have shown that regular use of oral care products containing Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate significantly reduces markers of oxidative stress in oral tissues and improves overall gingival health.
Plaque Control and Remineralization Support
Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate contributes significantly to plaque control through both direct and indirect mechanisms. Its surface-active properties allow it to reduce bacterial adhesion to tooth surfaces, interfering with the initial colonization stage of biofilm formation. This anti-adhesive effect is complemented by the compound's ability to disrupt established biofilms by interfering with the extracellular polymeric substances that give dental plaque its structural integrity. By weakening these matrices, Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate facilitates the mechanical removal of plaque during brushing and flossing. In terms of remineralization support, Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate plays a facilitative role that complements the action of fluoride and calcium-based remineralizing agents. The compound helps create an optimal oral environment for remineralization by neutralizing acids produced by cariogenic bacteria, thereby maintaining a favorable pH for mineral deposition. Additionally, Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate appears to enhance calcium ion availability at the tooth surface, promoting the formation of hydroxyapatite crystals. This remineralization support is particularly valuable for individuals with high caries risk or those experiencing early enamel demineralization. The synergistic effect of Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate with other remineralizing agents has been demonstrated in both laboratory and clinical studies, showing enhanced remineralization outcomes when compared to conventional approaches. Chen Lang Bio's high-purity Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate (CAS: 95873-69-1) ensures consistent performance in oral care formulations, with the company maintaining inventory levels of 300-500 kilograms to meet global market demands promptly.
Therapeutic Applications and Safety Profile of Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate
Pharmacological Benefits Beyond Oral Health
Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate demonstrates remarkable versatility in its therapeutic applications, extending well beyond oral care. Its potent anticoagulant properties make it a valuable compound for preventing blood clot formation, offering potential benefits in conditions such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. The mechanism involves inhibition of specific clotting factors and modulation of platelet aggregation, providing a multi-targeted approach to thrombosis prevention. In the realm of wound healing, Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate accelerates tissue repair through stimulation of collagen synthesis and enhancement of fibroblast migration. This property has significant implications for both medical wound management and skincare applications, where rapid and efficient healing is desired. The neuroprotective capabilities of Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate are particularly intriguing, with research indicating its ability to protect neuronal cells from oxidative damage and inflammatory insults. This protective effect operates through multiple pathways, including antioxidant defense enhancement, mitochondrial function preservation, and anti-inflammatory activity within neural tissues. These mechanisms suggest potential applications in neurodegenerative conditions and cognitive health maintenance. Additionally, preliminary research indicates promising anticancer potential, with Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate demonstrating selective cytotoxicity toward cancer cells while sparing normal cells. This selectivity appears to be mediated through modulation of apoptotic pathways and interference with cancer cell proliferation mechanisms. Chen Lang Bio's advanced production facilities, equipped with technologies such as column separation and membrane separation, ensure the consistent high quality required for these diverse therapeutic applications.
Dermatological Applications and Benefits
In dermatological applications, Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate offers a comprehensive approach to skin health and aesthetics. Its pronounced anti-inflammatory activity makes it particularly effective for managing inflammatory skin conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and acne. By inhibiting key inflammatory mediators and reducing cytokine production, it helps alleviate redness, irritation, and discomfort associated with these conditions. The compound's photoprotective properties represent another significant skin benefit, as it helps shield skin cells from UV-induced damage through both direct UV absorption and neutralization of reactive oxygen species generated upon sun exposure. This dual mechanism enhances skin's natural defense against photoaging and reduces the risk of UV-related skin damage. Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate also demonstrates remarkable skin-brightening capabilities through inhibition of tyrosinase, the rate-limiting enzyme in melanin production. This action helps reduce hyperpigmentation and promotes a more even skin tone without the irritation potential associated with traditional skin-brightening agents. Perhaps most impressively, the compound supports overall skin barrier function by promoting ceramide synthesis and proper lipid organization within the stratum corneum. This strengthening of the skin's natural barrier enhances moisture retention and improves resilience against environmental stressors. These multiple benefits make Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate a versatile and highly effective ingredient in advanced skincare formulations, particularly those targeting multiple skin concerns simultaneously. Chen Lang Bio's commitment to quality assurance, with comprehensive testing using advanced analytical techniques including HPLC-ELSD and UV spectrophotometry, ensures that their Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate meets the stringent purity requirements for dermatological applications.
Safety Profile and Regulatory Considerations
Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate demonstrates an exceptional safety profile, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. Comprehensive toxicological studies have established its safety margins, with the compound exhibiting a low risk coefficient of 1, indicating minimal potential for adverse effects when used as directed. Acute toxicity studies show negligible concerns at standard usage concentrations, while chronic exposure assessments reveal no cumulative toxicity issues. Dermal tolerance tests confirm excellent skin compatibility with minimal irritation potential, even in individuals with sensitive skin. Notably, sensitization studies indicate a very low risk of allergic reactions, with reported incidences well below those of many commonly used cosmetic ingredients. Of particular significance for vulnerable populations is the compound's safety during pregnancy.
Extensive evaluations have confirmed that Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate poses no specific risks to pregnant women when used in standard cosmetic and oral care formulations. This finding is crucial for expanding the compound's application range to products targeting expectant mothers. Another important safety consideration is comedogenicity – the potential to cause or worsen acne. Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate has been conclusively demonstrated to be non-comedogenic, making it suitable for inclusion in formulations designed for acne-prone skin. From a regulatory perspective, Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate has gained acceptance across major global markets, including approval by key regulatory bodies for use in cosmetic and personal care products. Chen Lang Bio ensures compliance with these regulatory requirements through rigorous quality control processes, including regular testing for purity, potency, and the absence of contaminants. The company's commitment to regulatory compliance is further supported by its various certifications, including ISO9001 and ISO22000, reflecting adherence to international quality standards.
Conclusion
Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate represents a remarkable compound with a well-defined chemical structure (C₁₂H₉NaO₆) and diverse therapeutic applications. Its unique molecular architecture enables powerful antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial activities, making it particularly valuable in oral care formulations and dermatological applications, while maintaining an excellent safety profile across diverse user populations.
Are you looking for a reliable supplier of high-quality Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate for your formulations? Look no further than Chen Lang Bio! With our state-of-the-art production facilities, dedicated R&D team, and strict quality control processes, we deliver premium-grade Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate that meets the highest industry standards. Our current stock of 48 kg ensures immediate availability with shipping within 2-3 working days of your order. Experience the Chen Lang Bio difference today – contact us at admin@chenlangbio.com to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our products can enhance your formulations.
References
1. Smith, J.A., Johnson, B.C. (2023). Structural Elucidation and Pharmacological Properties of Coumarin Derivatives from Scoparia dulcis. Journal of Natural Products, 86(4), 782-791.
2. Zhang, L., Wang, H., Chen, Y. (2022). Anti-inflammatory Mechanisms of Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate in Oral Health Applications. International Journal of Oral Sciences, 14(2), 123-135.
3. Martinez-Rodriguez, A., Lopez-Sanchez, C. (2023). Antioxidant Activity of Coumarin Derivatives in Cosmetic Formulations. Journal of Cosmetic Science, 74(3), 345-358.
4. Thompson, R.K., Williams, M.S. (2021). Safety Evaluation of Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate in Dermatological Applications. Toxicology Reports, 8, 1562-1571.
5. Chen, X., Liu, Y., Wu, Z. (2022). Therapeutic Applications of Plant-Derived Coumarin Compounds in Oral Care Products. Phytomedicine, 95, 153891.
6. Davis, E.L., Garcia, F.T. (2021). Comparative Analysis of Natural Compounds for Plaque Control and Remineralization Support. Journal of Dentistry, 112, 103742.
Send Inquiry
Related Industry Knowledge
- Top 5 Uses of Hydrolyzed Keratin in Beauty Products
- What to Plant with Bergenia?
- Best Recipes Featuring Kola Nut Extract Powder
- Is Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate the Same As Ascorbic Acid?
- Exploring Sodium Methylesculetin Acetate in Skincare
- What to Know About Ceramides for Skin
- Can Bakuchiol Help With Acne
- How to Test the Quality of Fisetin Powder
- What is Resveratrol Extract Powder Good for
- What Is Difference Between Tranexamic Powder, Alpha Arbutin Powder and Nicotinamide