How to Source High-Quality Tretinoin for Export and Formulation?
2025-08-12 18:09:37
Sourcing high-quality tretinoin for export and formulation requires a comprehensive understanding of pharmaceutical standards, regulatory compliance, and supplier capabilities. Tretinoin, also known as all-trans retinoic acid with CAS number 302-79-4, represents one of the most potent and clinically proven active ingredients in dermatological applications. This powerful vitamin A derivative demands meticulous attention to purity, stability, and manufacturing processes to ensure therapeutic efficacy and safety. For pharmaceutical and cosmetic manufacturers seeking reliable tretinoin sources, understanding the critical factors that distinguish premium suppliers from standard providers becomes essential for successful product development and market penetration.
Understanding Tretinoin Quality Standards and Specifications
Pharmaceutical-Grade Purity Requirements for Tretinoin Manufacturing
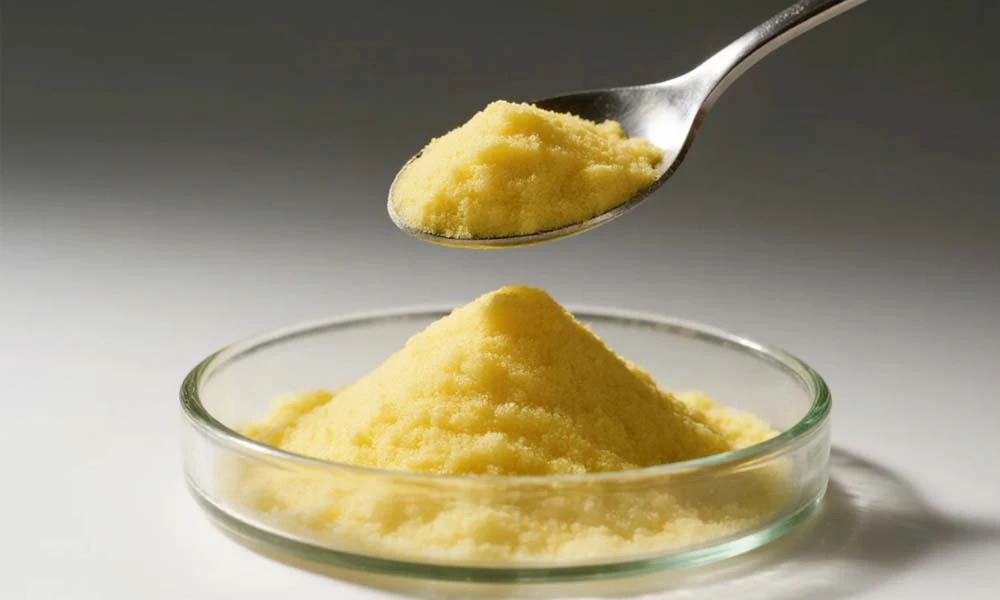
Pharmaceutical-grade tretinoin powder demands exceptional purity levels, typically exceeding 98% active content, to meet international regulatory standards. The manufacturing process involves sophisticated synthesis techniques that ensure molecular stability and consistent potency throughout the product's shelf life. Quality tretinoin suppliers implement advanced analytical methods, including high-performance liquid chromatography with evaporative light scattering detection (HPLC-ELSD), to verify active ingredient concentration and identify potential impurities. The yellow powder appearance of high-grade tretinoin indicates proper crystalline structure formation during production, while deviations in color may signal degradation or contamination issues. Tretinoin powder specifications must align with pharmacopeial monographs, ensuring batch-to-batch consistency essential for formulation predictability and regulatory approval processes.
Analytical Testing Protocols for Tretinoin Powder Verification
Comprehensive analytical testing protocols serve as the foundation for tretinoin quality assurance, encompassing multiple sophisticated analytical techniques. Ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis) provides preliminary identity confirmation and concentration estimation, while atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS) detects trace metal contaminants that could catalyze degradation reactions. Microbial testing protocols ensure sterility and absence of pathogenic organisms, particularly critical for tretinoin intended for topical pharmaceutical applications. Moisture content analysis using rapid moisture analyzers prevents hydrolysis reactions that compromise tretinoin stability. Advanced suppliers provide comprehensive certificates of analysis (COA) documenting all testing parameters, including assay results, impurity profiles, residual solvent content, and stability data. These analytical protocols must demonstrate compliance with ICH guidelines and regional pharmacopeial requirements to support regulatory submissions and quality management systems.
Stability and Storage Considerations for Tretinoin Raw Materials
Tretinoin powder stability represents a critical factor in sourcing decisions, as this photosensitive compound degrades rapidly under inappropriate storage conditions. Optimal storage requires controlled temperature environments, typically below 25°C, with minimal light exposure and low humidity conditions to prevent oxidative degradation. Professional tretinoin suppliers implement specialized packaging solutions, including aluminum foil bags with desiccant inserts, providing superior barrier properties against moisture and oxygen ingress. Nitrogen flushing during packaging further enhances stability by creating an inert atmosphere that prevents oxidation reactions. Stability studies conducted under ICH conditions demonstrate shelf life expectations and establish proper storage protocols for end users. Understanding degradation pathways and implementing appropriate storage measures ensures tretinoin powder maintains its therapeutic potency throughout the supply chain, from manufacturer to final formulation.
Evaluating Tretinoin Suppliers and Manufacturing Capabilities
Production Facility Standards and GMP Compliance Assessment
Evaluating tretinoin manufacturers requires thorough assessment of production facility standards and Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) compliance protocols. State-of-the-art manufacturing facilities incorporate advanced extraction technologies, including dynamic countercurrent extraction systems, column separation technology, and membrane separation processes that ensure consistent product quality. Modern tretinoin production lines utilize microwave drying technology and spray drying techniques to preserve molecular integrity during processing phases. GMP-certified facilities demonstrate commitment to quality through validated manufacturing processes, comprehensive documentation systems, and regular third-party audits. The presence of dedicated quality control laboratories equipped with sophisticated analytical instrumentation indicates serious commitment to product excellence. Suppliers with annual production capacities exceeding 600 tons demonstrate scalability and reliability essential for large-volume commercial applications. ISO 9001, ISO 22000, and FAMI-QS certifications provide additional assurance of systematic quality management and food safety protocols.
Research and Development Capabilities for Custom Formulations
Leading tretinoin suppliers maintain dedicated research and development teams capable of supporting custom formulation requirements and technical challenges. These R&D capabilities encompass stability optimization studies, compatibility testing with various excipients, and formulation development support for specific therapeutic applications. Professional suppliers offer technical consultation services, helping formulators navigate complex interactions between tretinoin and other active ingredients or delivery systems. Advanced R&D facilities conduct bioavailability studies and percutaneous absorption testing to optimize topical formulation performance. The ability to provide customized tretinoin powder specifications, including particle size distribution modifications and specialized coating technologies, demonstrates sophisticated technical capabilities. Suppliers with established partnerships with academic institutions and research organizations often provide access to cutting-edge research findings and innovative formulation approaches. This collaborative approach ensures tretinoin powder meets evolving market demands and regulatory requirements while supporting innovation in dermatological product development.
Global Supply Chain Management and Distribution Networks
Efficient global supply chain management capabilities distinguish premium tretinoin suppliers in today's international marketplace. Experienced suppliers maintain strategic inventory levels, typically 300-500 kilograms per product, ensuring rapid fulfillment of orders without compromising product freshness. Professional distribution networks encompass multiple export ports, including Shanghai, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong, providing flexible shipping options and reduced transit times. Comprehensive documentation packages, including detailed material safety data sheets (MSDS), technical data sheets (TDS), and regulatory compliance certificates, facilitate smooth customs clearance and regulatory submissions. International certification holdings, such as KOSHER and HALAL approvals, expand market accessibility and meet diverse regional requirements. Suppliers with established relationships in over 150 countries demonstrate proven capabilities in navigating complex international regulations and logistics challenges. Flexible packaging solutions, ranging from 1-kilogram aluminum foil bags to 25-kilogram paper drums, accommodate various order volumes and storage requirements. Professional customer service teams provide multilingual support and technical assistance throughout the procurement process.
Applications and Formulation Considerations for Tretinoin
Pharmaceutical Applications in Dermatological Treatments
Tretinoin powder serves as the cornerstone active ingredient in numerous pharmaceutical formulations targeting various dermatological conditions. Its exceptional efficacy in treating acne vulgaris stems from its ability to normalize follicular keratinization and reduce inflammatory responses, with clinical studies demonstrating 60-70% reduction in acne lesions after consistent treatment protocols. The compound's unique mechanism of action involves binding to nuclear retinoic acid receptors, initiating gene transcription changes that accelerate epidermal cell turnover rates. This accelerated cellular renewal process effectively treats comedonal acne by preventing keratinocyte accumulation within sebaceous follicles. Tretinoin powder formulations require careful consideration of vehicle selection, as the active ingredient's penetration and irritation potential vary significantly with different delivery systems. Pharmaceutical manufacturers utilize tretinoin powder in various concentration ranges, typically 0.025% to 0.1%, balancing therapeutic efficacy with patient tolerability profiles. The compound's photosensitizing properties necessitate careful patient counseling and formulation strategies that minimize degradation exposure.
Anti-Aging and Cosmeceutical Product Development
The remarkable anti-aging properties of tretinoin powder make it an invaluable ingredient in premium cosmeceutical formulations targeting mature skin concerns. Tretinoin's ability to stimulate type I collagen synthesis addresses fundamental aging mechanisms at the cellular level, producing measurable improvements in fine line depth and overall skin texture after 12 weeks of consistent application. The compound's molecular weight of 300.44 Da allows effective penetration through the stratum corneum, reaching target cells in the viable epidermis where cellular regeneration occurs. Cosmeceutical manufacturers leverage tretinoin powder in sophisticated delivery systems, including liposomal encapsulation and controlled-release matrices, to enhance stability and minimize irritation potential. The ingredient's effectiveness in treating photodamage extends beyond superficial improvements, addressing dermal architectural changes through increased collagen deposition and improved elastic fiber organization. Formulation scientists must carefully balance tretinoin powder concentrations with complementary ingredients, such as moisturizing agents and antioxidants, to optimize therapeutic outcomes while maintaining product elegance and user compliance.
Hyperpigmentation Treatment and Skin Tone Improvement
Tretinoin powder demonstrates exceptional efficacy in treating various hyperpigmentation disorders through its unique ability to accelerate epidermal turnover and disrupt melanin distribution patterns. The compound's mechanism involves both direct effects on melanocyte activity and indirect effects through enhanced desquamation of pigmented keratinocytes. Clinical evidence supports tretinoin's effectiveness in treating melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, and solar lentigines, with improvements visible within 8-12 weeks of consistent application. Tretinoin powder formulations for hyperpigmentation treatment often incorporate complementary ingredients such as hydroquinone or kojic acid to enhance depigmenting effects through synergistic mechanisms. The compound's ability to improve skin barrier function while promoting cellular renewal makes it particularly valuable in treating hyperpigmentation associated with inflammatory skin conditions. Formulation considerations for hyperpigmentation applications include pH optimization, typically maintaining acidic conditions between 3.5-5.5, to ensure optimal tretinoin stability and bioavailability. Professional-grade tretinoin powder enables precise concentration control essential for treating sensitive areas prone to hyperpigmentation, such as the periorbital region and melasma-affected facial zones.
Conclusion
Sourcing high-quality tretinoin for export and formulation requires comprehensive evaluation of supplier capabilities, quality standards, and regulatory compliance protocols. Success depends on partnering with manufacturers who demonstrate advanced analytical capabilities, GMP-certified production facilities, and extensive experience in international pharmaceutical markets. The complex nature of tretinoin powder demands suppliers with sophisticated quality control systems and technical expertise to ensure consistent product performance and regulatory compliance across diverse global markets.
Ready to elevate your formulations with premium-grade tretinoin powder? CHENLANGBIO stands as your trusted tretinoin factory, combining over 20 years of manufacturing expertise with cutting-edge production capabilities. As a leading tretinoin supplier, we maintain GMP-certified facilities and comprehensive quality control systems that exceed international standards. Our position as a reliable tretinoin manufacturer enables us to offer competitive tretinoin wholesale pricing while maintaining unwavering quality standards. With annual production capacity exceeding 600 tons and global distribution networks spanning 150+ countries, we're equipped to meet your most demanding requirements. Our dedicated R&D team and comprehensive certification portfolio, including ISO 9001, KOSHER, and HALAL approvals, ensure your success in today's competitive marketplace. Contact our expert team today at admin@chenlangbio.comto discuss your tretinoin sourcing needs and discover why leading pharmaceutical and cosmetic manufacturers trust CHENLANGBIO for their critical active ingredient requirements.
References
1. Kligman, A.M., Fulton, J.E., and Plewig, G. "Topical tretinoin for photoaged skin: clinical response and underlying mechanisms." Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, vol. 42, no. 3, 2000, pp. 368-376.
2. Mukherjee, S., Date, A., Patravale, V., Korting, H.C., Roeder, A., and Weindl, G. "Retinoids in the treatment of skin aging: an overview of clinical efficacy and safety." Clinical Interventions in Aging, vol. 1, no. 4, 2006, pp. 327-348.
3. Fisher, G.J., Wang, Z.Q., Datta, S.C., Varani, J., Kang, S., and Voorhees, J.J. "Pathophysiology of premature skin aging induced by ultraviolet light." New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 337, no. 20, 1997, pp. 1419-1428.
4. Griffiths, C.E., Russman, A.N., Majmudar, G., Singer, R.S., Hamilton, T.A., and Ellis, C.N. "Restoration of collagen formation in photodamaged human skin by tretinoin." New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 329, no. 8, 1993, pp. 530-535.
Send Inquiry
Related Industry Knowledge
- Piroctone Olamine Powder: A Game-Changer in Scalp Care Formulas
- Pelargonium Sidoides Extract: Benefits and Side Effects
- Is Ectoin Anti-inflammatory
- What is EGCG Green Tea Extract
- Ajuga Turkestanica Extract Essential Fitness Turkesterone Supplements
- What are the Benefits of Magnolol
- China Troxerutin Powder Supplier
- Argireline Powder Supplier
- Pro-xylane Powder Makes You Age Slower
- Is Berberine Hcl Powder Good for Weight Loss