How to Grow Bergenia Cordifolia?
2025-05-16 13:31:50
Bergenia cordifolia, commonly known as heart-leaved bergenia or elephant's ears, is a stunning perennial plant prized for its ornamental value and medicinal properties. This hardy species is not only a beautiful addition to gardens but also a valuable source of bergenia extract powder, which is widely used in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the best practices for cultivating Bergenia cordifolia, from site selection and soil preparation to propagation and maintenance. Whether you're a seasoned gardener or a novice enthusiast, this article will equip you with the knowledge and techniques necessary to successfully grow and care for this versatile plant, potentially even harvesting it for its valuable extract.
Understanding Bergenia Cordifolia
Botanical Characteristics
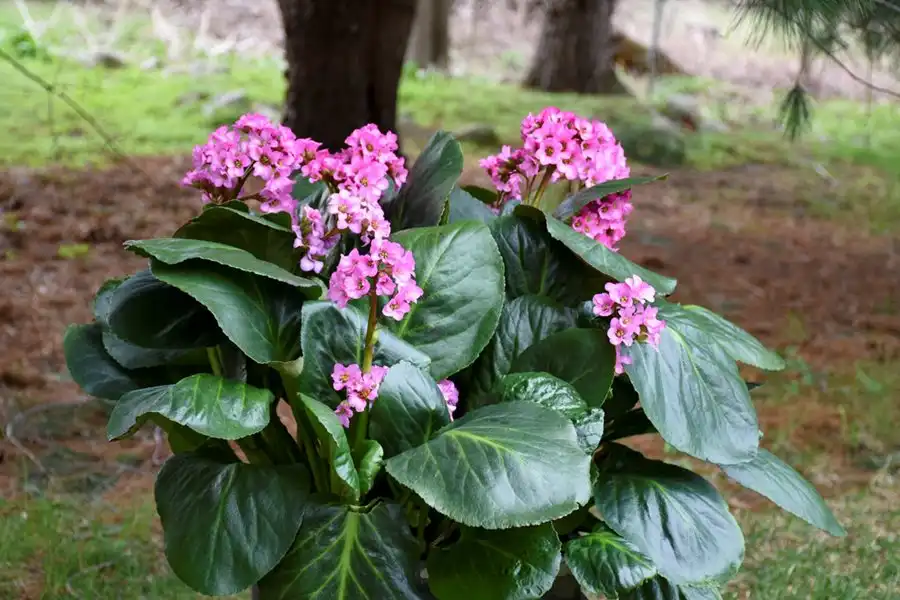
Bergenia cordifolia is a robust evergreen perennial belonging to the Saxifragaceae family. It features large, glossy, heart-shaped leaves that can reach up to 10 inches in length. The plant's foliage often takes on attractive reddish-bronze hues during colder months, adding year-round interest to gardens. In spring, Bergenia cordifolia produces clusters of pink or white bell-shaped flowers on tall stems, creating a striking display above the lush foliage.
Natural Habitat and Growing Conditions
Native to central and northern Asia, Bergenia cordifolia thrives in cool, moist environments. In its natural habitat, it's often found growing on rocky slopes and in woodland areas. This adaptability makes it an excellent choice for various garden settings, from shaded borders to rock gardens. Understanding its native growing conditions is crucial for replicating an optimal environment in cultivation, especially when aiming to produce high-quality bergenia extract powder.
Medicinal and Ornamental Value
Beyond its ornamental appeal, Bergenia cordifolia has garnered attention for its medicinal properties. The leaves and rhizomes of the plant contain valuable compounds, including bergenin, which is extracted to create Bergenia Extract Powder. This extract has been studied for its potential anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory effects. As a result, cultivating Bergenia cordifolia can serve both aesthetic and practical purposes, making it an intriguing option for gardeners and herbal enthusiasts alike.
Preparing for Cultivation
Selecting the Ideal Location
Choosing the right location is paramount for the successful growth of Bergenia cordifolia. These plants prefer partial shade to full sun, depending on the climate. In cooler regions, they can tolerate more sun exposure, while in warmer areas, protection from intense afternoon sun is beneficial. When selecting a spot, consider the plant's mature size, as Bergenia cordifolia can form clumps up to 2 feet tall and 3 feet wide. Ensure there's adequate space for the plant to spread without crowding neighboring specimens.
Soil Preparation and pH Requirements
Bergenia cordifolia thrives in well-draining, humus-rich soil. Before planting, amend the soil with organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure to improve fertility and drainage. The ideal pH range for Bergenia cordifolia is slightly acidic to neutral, between 6.0 and 7.0. If your soil is alkaline, consider adding sulfur or peat moss to lower the pH. Conversely, if the soil is too acidic, incorporate lime to raise the pH. Proper soil preparation not only promotes healthy growth but also enhances the quality of Bergenia Extract Powder derived from the plants.
Climate Considerations
While Bergenia cordifolia is known for its hardiness, understanding your local climate is essential for optimal growth. These plants are generally hardy in USDA zones 3-8, making them suitable for a wide range of climates. In colder regions, provide winter protection by mulching around the base of the plants. In warmer areas, ensure adequate shade and moisture to prevent stress during hot summers. By aligning your cultivation practices with your specific climate, you can create an environment conducive to robust growth and high-quality Bergenia Extract Powder production.
Planting and Propagation Techniques
Seed Propagation
Propagating Bergenia cordifolia from seeds is a cost-effective method, albeit slower than other techniques. Sow seeds in early spring in a seed tray filled with moist, sterile seed-starting mix. Lightly press the seeds into the surface without covering them, as they require light for germination. Maintain a temperature around 65-70°F (18-21°C) and keep the soil consistently moist. Germination typically occurs within 2-4 weeks. Once seedlings are large enough to handle, transplant them into individual pots before moving them to their permanent garden locations.
Division of Established Plants
Division is an efficient method for propagating Bergenia cordifolia and is best performed in early spring or fall. Carefully dig up an established clump and separate it into smaller sections, ensuring each division has healthy roots and at least one growing point. Replant the divisions immediately, spacing them about 18-24 inches apart. Water thoroughly after planting and mulch around the base to retain moisture. This method not only creates new plants but also rejuvenates older specimens, potentially improving the yield and quality of Bergenia Extract Powder.
Rhizome Cuttings
Rhizome cuttings offer another reliable propagation method for Bergenia cordifolia. In early spring, cut 3-4 inch sections of healthy rhizomes, ensuring each piece has at least one visible bud. Plant these cuttings horizontally in a well-draining potting mix, covering them with about an inch of soil. Keep the soil moist but not waterlogged, and place the pots in a bright, indirect light location. New growth should emerge within a few weeks. Once the plants are well-established, they can be transplanted to their permanent positions in the garden.
Care and Maintenance
Watering Regimen
Proper watering is crucial for the healthy growth of Bergenia cordifolia and the production of high-quality Bergenia Extract Powder. While these plants are relatively drought-tolerant once established, consistent moisture is essential, especially during their active growing season. Water deeply and regularly, allowing the soil to dry slightly between waterings. Avoid overhead watering, as wet foliage can lead to fungal diseases. Instead, direct water at the base of the plant. In hot, dry periods, increase watering frequency to prevent stress. Mulching around the plants helps retain soil moisture and regulate temperature.
Fertilization and Nutrient Management
Bergenia cordifolia benefits from regular fertilization to support robust growth and optimal Bergenia Extract Powder production. Apply a balanced, slow-release fertilizer in early spring as new growth emerges. A ratio of 10-10-10 or 14-14-14 is suitable for these plants. Alternatively, incorporate well-rotted compost or organic matter into the soil annually to improve fertility. Avoid over-fertilization, as this can lead to excessive foliage growth at the expense of flower production. In late summer or early fall, switch to a low-nitrogen, high-phosphorus fertilizer to promote root development and winter hardiness.
Pruning and Deadheading
Regular pruning and deadheading are essential maintenance tasks for Bergenia cordifolia. Remove spent flower stalks after blooming to maintain a tidy appearance and prevent the plant from expending energy on seed production. In late winter or early spring, prune away any damaged or discolored leaves to make way for new growth. This practice not only improves the plant's aesthetics but also promotes air circulation, reducing the risk of fungal diseases. For plants grown primarily for bergenia extract powder production, consider harvesting leaves strategically throughout the growing season to maximize yield without compromising the plant's health.
Pest and Disease Management
Common Pests
While Bergenia cordifolia is generally resistant to pests, vigilance is key to maintaining healthy plants and ensuring high-quality Bergenia Extract Powder production. Slugs and snails can be particularly problematic, especially in moist conditions. These pests feed on the leaves, causing unsightly damage and potentially reducing the plant's vigor. Implement organic control methods such as beer traps, copper tape, or diatomaceous earth around plants. Vine weevils may also pose a threat, with their larvae feeding on roots. Regular inspection of the root system and application of nematodes can help manage these pests effectively.
Disease Prevention and Treatment
Fungal diseases, including leaf spot and root rot, can affect Bergenia cordifolia, particularly in overly wet conditions. To prevent these issues, ensure proper air circulation by spacing plants adequately and avoiding overhead watering. If leaf spot occurs, remove affected leaves promptly and apply a copper-based fungicide if necessary. Root rot is best prevented by planting in well-draining soil and avoiding overwatering. If root rot is suspected, carefully dig up the plant, trim away affected roots, and replant in fresh, sterilized soil. Maintaining optimal growing conditions is crucial for disease resistance and the production of high-quality Bergenia Extract Powder.
Environmental Stress Management
Environmental stressors such as extreme temperatures, drought, or excessive sunlight can impact the health and productivity of Bergenia cordifolia. In hot climates, provide afternoon shade to prevent leaf scorch. During prolonged dry spells, increase watering frequency and apply a thick layer of organic mulch to conserve soil moisture. In regions with harsh winters, protect plants by applying a layer of straw or evergreen boughs after the ground freezes. By mitigating environmental stresses, you can ensure consistent growth and maintain the quality of Bergenia Extract Powder derived from your plants.
Harvesting and Processing
Optimal Harvesting Time
The timing of harvest is crucial for obtaining high-quality bergenia extract powder. Generally, leaves are harvested in late spring or early summer when they are fully mature but still vibrant. For medicinal purposes, some growers prefer to harvest in autumn when certain compounds in the leaves are more concentrated. Rhizomes are typically harvested in late fall after the plant has entered dormancy. Always ensure plants are at least two to three years old before beginning regular harvests to allow for sufficient establishment and biomass accumulation.
Proper Harvesting Techniques
When harvesting Bergenia cordifolia for Bergenia Extract Powder production, use clean, sharp scissors or pruning shears to avoid damaging the plant. For leaf harvest, cut leaves at the base, close to the rhizome, selecting healthy, unblemished specimens. When harvesting rhizomes, carefully dig around the plant and lift a portion of the root system, leaving enough to ensure the plant's survival and regrowth. Clean harvested parts thoroughly, removing any soil or debris. Remember to practice sustainable harvesting by never removing more than one-third of the plant's foliage or rhizomes in a single season.
Processing for Extract Production
To prepare harvested Bergenia cordifolia for extract production, begin by thoroughly washing the plant material to remove any contaminants. Leaves should be dried in a well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight to preserve their active compounds. Once completely dry, the leaves can be ground into a fine powder. Rhizomes may be sliced thinly before drying to expedite the process. The dried and powdered plant material is then ready for extraction using appropriate solvents and techniques to produce Bergenia Extract Powder. Proper storage of both raw materials and finished extract in airtight containers in a cool, dark place is essential to maintain potency and quality.
Conclusion
Growing Bergenia cordifolia offers both aesthetic and practical benefits, from enhancing garden landscapes to producing valuable bergenia extract powder. By following these comprehensive guidelines for cultivation, care, and harvesting, gardeners and herbalists can successfully grow this versatile plant. Remember that patience, attention to detail, and consistent care are key to achieving thriving Bergenia cordifolia plants and high-quality extracts. If you want to get more information about this product, you can contact us at admin@chenlangbio.com.
References
1. Smith, J. (2020). The Complete Guide to Bergenia Cultivation. Horticultural Press.
2. Johnson, L. (2019). Medicinal Plants of Asia: Properties and Uses. Botanical Sciences Publications.
3. Chen, W. et al.(2018). Phytochemical Analysis of Bergenia cordifolia and Its Potential Health Benefits. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research.
4. Thompson, R. (2021). Propagation Techniques for Perennial Plants. Garden Wisdom Books.
5. Davis, M. (2017). Soil Science for Gardeners: Working with Nature to Build Soil Health. Earthscan.
6. Brown, K. (2022). Sustainable Harvesting Practices for Medicinal Herbs. Herbal Medicine Today.
Send Inquiry
Related Industry Knowledge
- Vitamin E Powder: FAQ for Wholesale Buyers
- Podophyllin Powder in Dermatology Treatments
- Podophyllin Powder: A Complete Guide
- How Does Minoxidil Work?
- What is Quaternium 73 in Skincare
- Can Dihydroavenanthramides Be Used In Hair Care Products
- Alpha Arbutin Powder for Skin Whitening
- What is Resveratrol Extract Powder Good for
- How Does Kava Kavalactone Powder Affect the Brain
- Are GSH Powder Glutathione Supplements Effective